Video
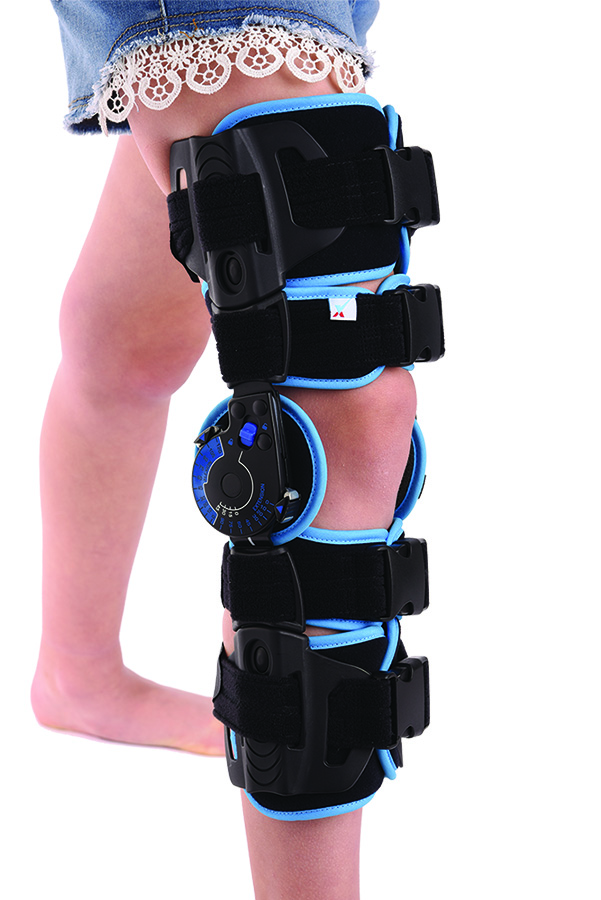
Lightweight adjustable telescopic knee brace for children, featuring four adjustable padded foam cuffs. Easy to fit, one size fits most.
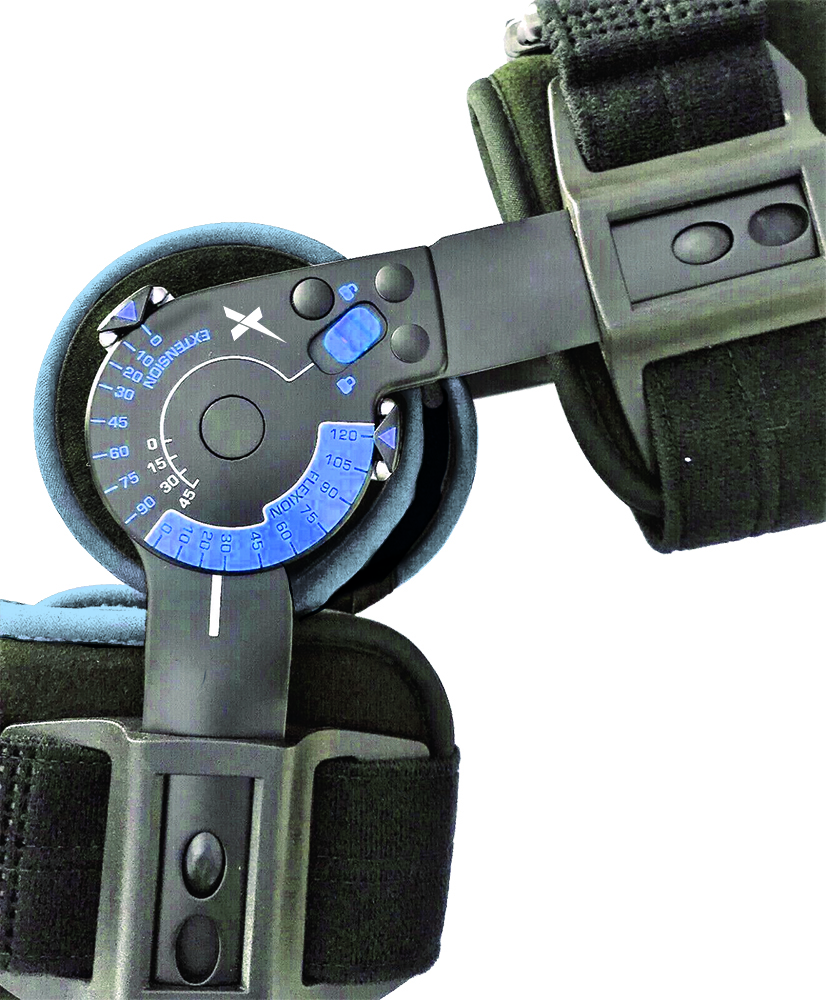
Paediatric Telescopic ROM Knee Brace
Lightweight adjustable telescopic knee brace for children, featuring four adjustable padded foam cuffs. Easy to fit, one size fits most.
£94.95
Size Guide
| Length (cm) | ||||
| Size | Min | Max | Product Code | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Universal | 35 | 45 | PKRB/UNI | |
-
Features & Benefits
- Lightweight adjustable telescopic knee brace with a monocentric joint offering range of movement control from 0° to 90° in extension and 0° to 120° in flexion with lockable increments of 15°.
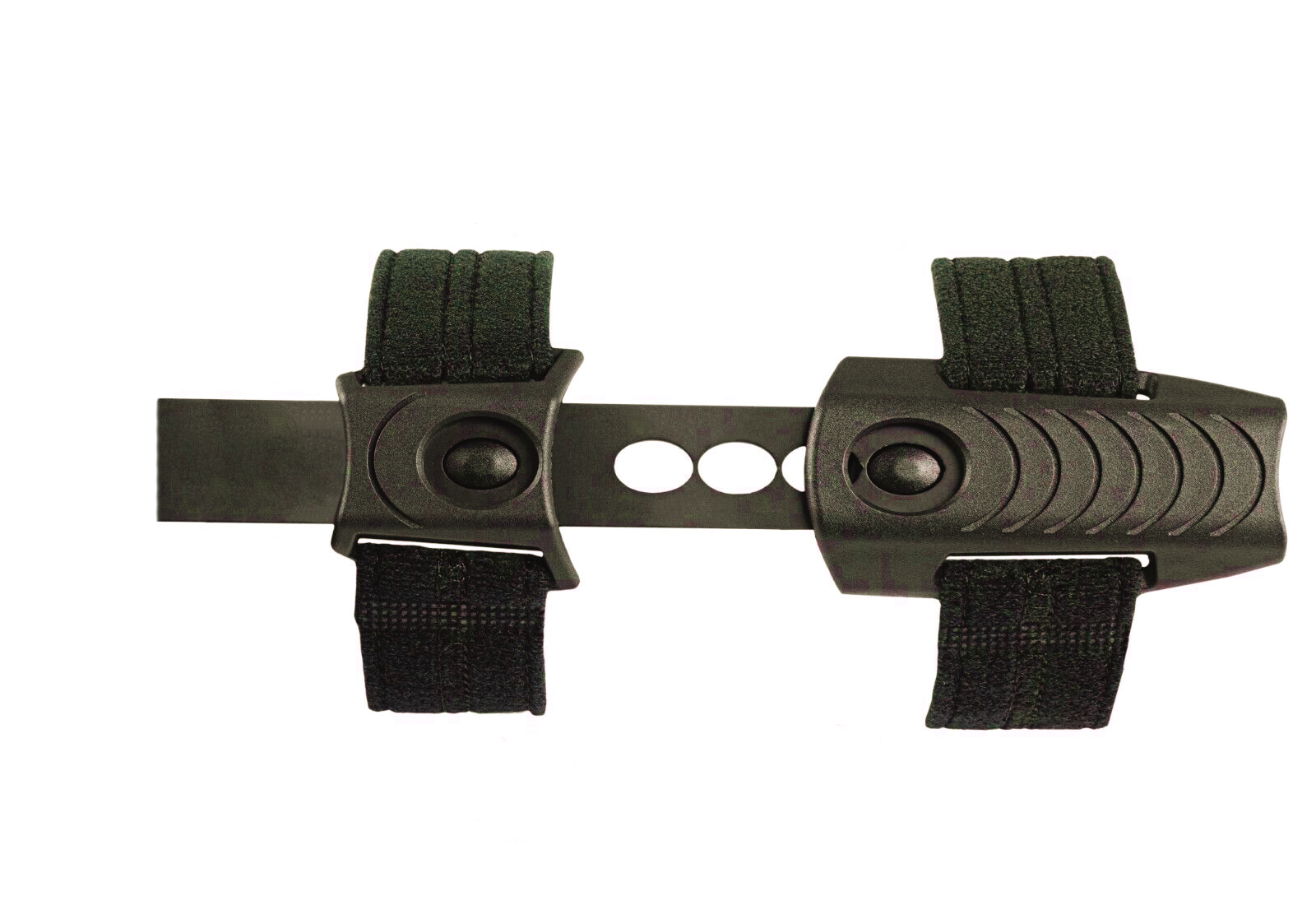
- Features four adjustable padded foam cuffs which can be positioned as required for optimum comfort and support.
- One size fits all, with a minimum length of 35cm and a maximum extended length of 45cm.
-
Indications for Use
Unstable or injured knees, post-operative, post injury rehabilitation, knee ligament injuries, hyperextension.